FORM DRC 09 in GST
- 14 Jul 25
- 7 mins

FORM DRC 09 in GST
Key Takeaways
- FORM GST DRC-09 is used to recover unpaid GST dues through government-linked organisations.
- It is issued under Section 79(1)(a) of the CGST Act when a taxpayer fails to pay after a demand notice.
- The form authorises a specified officer to deduct dues from payments owed to the defaulter.
- DRC-09 enables indirect recovery by attaching funds already payable to the defaulter by public bodies.
- Understanding DRC-09 ensures better compliance and prevents legal escalation in GST recovery proceedings.
Under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework, taxpayers are responsible for self-assessment and timely payment of dues. However, in cases of non-payment or short payment, whether deliberate or accidental, the tax officer after issuance empowers authorities to recover the dues.
Section 79 of the GST Act outlines specific recovery procedures, including the issuance of FORM GST DRC-09. This form authorises a specified officer to recover voluntary tax payments from the defaulter. Recovery action typically begins three months after a demand notice, ensuring timely compliance and protecting government revenue.
This article explains the purpose and process of FORM DRC-09 in the GST recovery mechanism.
What is DRC in GST?
India uses Demand and Recovery Forms (DRCs) to manage and enforce the GST regime. The tax department sends a notice to companies if they have not paid their GST dues. This certificate action helps the jurisdictional officer recover unpaid GST dues.
For this purpose, there are several DRC forms from DRC-01 to DRC-20, which state the provisions of rule. These purposes include penalty imposition, issuance of tax notices, resolution of disputes, recovery of unpaid dues and more. The government has about 28 DRC forms under this tax regime, with some still to be introduced.
Furthermore, the land revenue authority enforces these provisions of rule upon the default person. Hence, this is an important part of the GST system for proper tax collection and prevention of tax evasion. This way, the government can recover and track any unpaid taxes.
Introduction to FORM GST DRC – 09
Form DRC 09 in GST is a recovery tool invoked under Section 79(1)(a) of the CGST Act. It authorises a proper officer to recover government dues outstanding from a taxpayer (defaulter) using recovery forms. A "specified officer" is instructed to deduct the amount outstanding from any amount payable to the defaulter. A taxpayer fails to make voluntary payments despite receiving a demand notice.
The specified officer is identified under Rule 143 of the CGST Rules in DRC–09 as an action under clause. These include officers belonging to the Central Government, State Governments, Union Territory administrations, and local authorities.
Moreover, it includes organisations like Boards, Corporations, or companies fully or partially owned or controlled by these governments. The GST DRC-09 Form is a provisional attachment which achieves indirect recovery of dues by aiming at already payable funds to the defaulter from government-related bodies.
It is an important instrument in the hands of tax officers, allowing for GST compliance enforcement and recovery of overdue amounts through payment in instalments. Tax officials use GST DRC-09 Form to ensure the government accepts it as an acceptance of payment made to recover its revenue, even when a taxpayer does not make a direct payment. After the payment is successful, a certificate of payment is shared with you indicating your compliance.
Legal Basis – Section 79
Section 79 of the Indian Penal Code protects a taxable person who, acting in good faith, performs an act believing it is lawful due to a mistaken belief about the law. You will not attract any legal action if you act honestly, based on a factual error and not a misunderstanding of the Notice for attachment and Notice for Auction.
For instance, if a person captures another thinking that he has committed a crime while actually in self-defence, then the captor can make a Rectification of Demand Order, Request for Rectification or Application for Rectification.
A request for rectification hyperlink is shared, where the acceptance of the rectification filed will be recorded. Following this process, an acceptance of rectification filed intimated will be shared with you. If the rejection of application for Request for Rectification happens, the Adjucating Authority will proceed with the show-cause notice. This provision maintains the doctrine of honest intention in juristic acts.

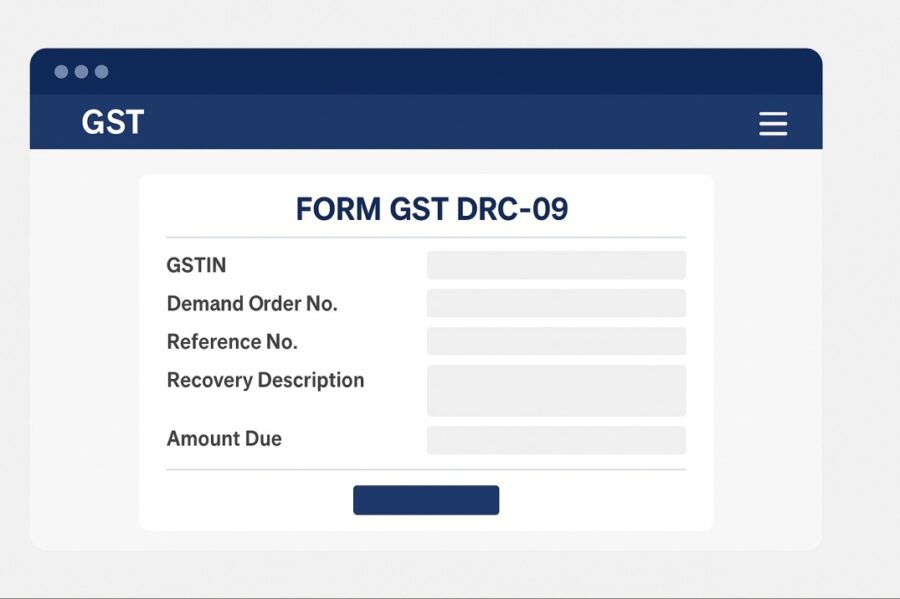
Sample Format of FORM GST DRC – 09
The DRC 09 prescribed form requires your GSTIN, name, demand order number, reference number of recovery and other details for recovering tax on immovable properties. Here is a sample of FORM DRC 09 in GST for imposition of penalty:
Conclusion
Summing up, FORM DRC 09 in GST is critical for the recovery process under the GST regime. The proper officer issues this form as a fresh notice to recover dues efficiently through designated government-linked organisations. Moreover, the government and tax officers ensure that unpaid taxes are not left unpaid, safeguarding receipts and ensuring compliance under the prescribed form.
Knowledge of its role and statutory support through Section 79 is important for professionals and taxpayers. Knowing these forms helps avoid problems and makes tax administration smoother. For further information, always consult authoritative GST guidelines or a tax consultant.
💡If you want to streamline your invoices and make payments via credit or debit card or UPI, consider using the PICE App. Explore the PICE App today and take your business to new heights.